
Subject–auxiliary inversion (also called subject–operator
inversion) is a frequently occurring type of
inversion in
English, whereby a finite
auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the
copula be – appears to "invert" (change places) with the
subject.[1]
The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the
opposite of the canonical SV (subject–verb)
order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of
subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of
questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation
of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with
negative expressions (negative
inversion).
In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible
with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on
subject-verb inversion.
Overview
Subject–auxiliary inversion involves placing the subject after a
finite auxiliary verb,[2]
rather than before it as is the case in typical declarative sentences
(the canonical word order of English being
subject–verb–object). The auxiliary verbs which may participate in
such inversion (e.g. is, can, have, will,
etc.) are described at
English auxiliaries and contractions. Note that forms of the verb
be are included regardless of whether or not they function as
auxiliaries in the sense of governing another verb form. (For exceptions
to this restriction, see
Inversion with other types of verb below.)
A typical example of subject–auxiliary inversion is given below.
-
- a. Sam has read the paper. - Statement
- b. Has Sam read the paper? - Yes–no question
formed using inversion
Here the subject is Sam, and the verb has is an
auxiliary. In the question, these two elements change places (invert).
If the sentence does not have an auxiliary verb, this type of simple
inversion is not possible. Instead, an auxiliary must be introduced into
the sentence in order to allow inversion:[3]
-
- a. Sam enjoys the paper. - Statement with the
non-auxiliary verb enjoys
- b. *Enjoys Sam the paper? - This is incorrect;
simple inversion not possible with this type of verb
- c. Does Sam enjoy the paper? - The sentence
formulated with the auxiliary does now allows inversion
For details of the use of do, did and does for
this and similar purposes, see
do-support. For exceptions to the principle that the inverted
verb must be an auxiliary, see
Inversion involving non-auxiliary verbs below. It is also possible
for the subject to invert with a negative contraction (can't,
isn't, etc.). For example:
-
- a. He isn't nice.
- b. Isn't he nice? - The subject he
inverts with the negated auxiliary contraction isn't
Compare this with the uncontracted form Is he not nice? and
the archaic Is not he nice?).
Uses of subject–auxiliary inversion
The main uses of subject–auxiliary inversion in English are described
in the following sections, although other types can occasionally be
found.[4]
It should be noted that most of these uses of inversion are restricted
to main clauses; they are not found in
subordinate clauses. However other types (such as inversion in
condition clauses) are specific to subordinate clauses.
In questions
The most common use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in
question formation. It appears in
yes–no questions:
-
- a. Sam has read the paper. - Statement
- b. Has Sam read the paper? - Question
and also in questions introduced by other interrogative words (wh-questions):
-
- a. Sam is reading the paper. - Statement
- b. What is Sam reading? - Question introduced
by interrogative what
Inversion does not occur, however, when the interrogative word is the
subject or is contained in the subject. In this case the subject remains
before the verb (it can be said that
wh-fronting takes precedence over subject–auxiliary
inversion):
-
- a. Somebody has read the paper. - Statement
- b. Who has read the paper? - The subject is
the interrogative who; no inversion
- c. Which fool has read the paper? - The
subject contains the interrogative which; no inversion
Inversion also does not normally occur in
indirect questions. For example:
-
- a. "What did Sam eat?", Cathy wonders. -
Inversion in a direct question
- b. *Cathy wonders what did Sam eat. -
Incorrect; inversion should not be used in an indirect question
- c. Cathy wonders what Sam ate. - Correct;
indirect question formed without inversion
Similarly:
-
- a. We asked whether Tom had left. - Correct;
indirect question without inversion
- b. *We asked whether had Tom left. - Incorrect
Negative inversion
Another use of subject–auxiliary inversion is in sentences which
begin with certain types of expressions which contain a negation or have
negative force. For example
-
- a. Jessica will say that at no time.
- b. At no time will Jessica say that. -
Subject-auxiliary inversion with a fronted negative expression.
This is described in detail at
negative inversion.
Inversion in condition clauses
Subject–auxiliary inversion can be used in certain types of
subordinate clause expressing a condition:
-
- a. If the general had not ordered the advance,...
- b. Had the general not ordered the advance,...
- Subject-auxiliary inversion of a counterfactual conditional
clause
Note that when the condition is expressed using inversion, the
conjunction if is omitted. More possibilities are given at
English conditional sentences: Inversion in condition clauses, and
variations are described at
English subjunctive: Inversion.
Other cases
Subject–auxiliary inversion is used after the
anaphoric particle so, mainly in
elliptical sentences. The same frequently occurs in elliptical
clauses beginning with as.
-
- a. Fred fell asleep, and Jim fell asleep too.
- b. Fred fell asleep, and so did Jim.
- c. Fred fell asleep, as did Jim.
Inversion also occurs following an expression beginning with so
or such, as in:
-
- a. We felt so tired (such tiredness) that we fell asleep.
- b. So tired (Such tiredness) did we feel that we fell
asleep.
Subject–auxiliary inversion may optionally be used in elliptical
clauses introduced by the particle of comparison than:
-
- a. Sally knows more languages than her father does.
- b. Sally knows more languages than does her father.
- Optional inversion, with no change in meaning
Inversion with other types of verb
There are certain sentence patterns in English in which subject–verb
inversion takes place where the verb is not restricted to an auxiliary
verb. Here the subject may invert with certain main verbs, e.g. After
the pleasure comes the pain, or with a chain of verbs, e.g.
In the box will be a bottle. These are described in the
article on
subject-verb inversion. Further, inversion was not limited to
auxiliaries in older forms of English. Examples of non-auxiliary verbs
being used in typical subject–auxiliary inversion patterns may be found
in older texts or in English written in an archaic style:
-
- Know you what it is to be a child? (Francis
Thompson)
The verb have, when used to denote broadly defined
possession (and hence not as an auxiliary), is still sometimes used
in this way in modern standard English:
-
- Have you any idea what this would cost?
Inversion as a remnant of V2 word order
In some cases of subject–auxiliary inversion, such as negative
inversion, the effect is to put the finite auxiliary verb into second
position in the sentence. In these cases, inversion in English results
in word order that is like the
V2 word order of other
Germanic languages (Danish, Dutch, Frisian, Icelandic, German,
Norwegian, Swedish, Yiddish, etc.). These instances of inversion are
remnants of the V2 pattern that formerly existed in English as it still
does in its related languages.
Old English followed a consistent V2 word order.
Structural
analyses
The structural analysis of subject-auxiliary inversion, and of
inversion in general, challenges many theories of sentence structure, in
particular, those theories based on
phrase structure. The challenge stems from the fact that these
theories posit the existence of a finite
verb phrase
constituent. The standard declarative sentence is divided into two
immediate constituents, a subject NP and a
predicate VP. When subject-auxiliary inversion occurs, it appears to
violate the integrity of the predicate.[5]
The canonical predicate is underlined in the following sentences:
-
- a. Larry has started working. - Traditional VP
predicate is a continuous combination of words.
- b. Has Larry started working? -
Traditional VP predicate is no longer continuous.
-
- a. Susan will listen to the music. -
Traditional VP predicate is a continuous combination of words.
- b. Will Susan listen to the music? -
Traditional VP predicate is no longer continuous.
The finite VP predicate is a continuous sequence of words in the
a-sentences. In the b-sentences in contrast, subject-auxiliary inversion
breaks up the predicate. What this means is that in one sense or
another, a
discontinuity is present in the structure.
One widespread means of addressing this difficulty is to posit
movement. The underlying word order of the b-sentences is deemed to be
that shown in the a-sentences. To arrive at the inversion word order in
the b-sentences, movement is assumed.[6]
The finite verb moves out of its base position after the subject into a
derived position in front of the subject.
-
-

By moving out of its base position and into the derived position at
the front of the clause, the integrity of the predicate VP constituent
can be maintained, since it is present at an underlying level of
sentence structure.
An alternative analysis does not acknowledge the binary division of
the clause into subject NP and predicate VP, but rather it places the
finite verb as the root of the entire sentence and views the subject as
switching to the other side of the finite verb. No discontinuity is
perceived.
Dependency grammars are likely to pursue this sort of analysis.[7]
The following dependency trees illustrate how this alternative account
can be understood:
-
-
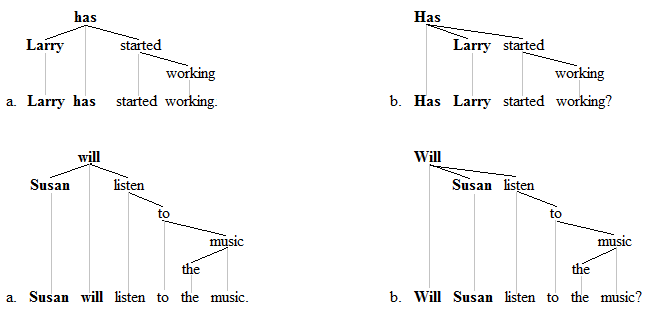
These trees show the finite verb as the root of all sentence
structure. The hierarchy of words remains the same across the a- and
b-trees. If movement occurs at all, it occurs rightward (not leftward);
the subject moves rightward to appear as a post-dependent of its head,
which is the finite auxiliary verb.
See also
Notes
-
^ For accounts and
discussion of subject-auxiliary inversion, see for instance
Quirk and Greenbaum (1979:63), Radford (1988:32f.), Downing and
Locke (1992:22f.), Ouhalla (1994:62ff.).
-
^ Concerning the
obligatory status of the verb that undergoes inversion as an
auxiliary, see Radford (1988:149f.).
-
^ Concerning do-support,
see for instance Bach (1974:94), Greenbaum and Quirk (1990:232),
Ouhalla (1994:62ff.).
-
^ Concerning the
environments illustrated here in which subject-auxiliary
inversion can or must occur, they are illustrated and discussed
in numerous places in the literature, e.g. Bach (1974:93), Quirk
et al. (1979:378f.), Greenbaum and Quirk (1990:232, 410f.),
Downing and Locke (1992:22f, 230f.).
-
^ Concerning the
difficulty that inversion generates for theories of syntax that
build on the binary subject-predicate division of the clause,
see Lockwood (2002:52).
-
^ For examples of
the movement-type analysis of subject-auxiliary inversion, see
for instance Ouhalla (1994:62ff.), Culicover (1997:337f.), Adger
(2003:294), Radford (1988: 411ff., 2004: 123ff).
-
^ Concerning the
dependency grammar analysis of inversion, see Groß and Osborne
(2009: 64-66).
References
- Adger, D. 2003. Core syntax:A minimalist approach. Oxford,
UK: Oxford University Press.
- Bach, E. 1974. Syntactic theory. New York: Holt, Rinehart
and Winston, Inc.
- Culicover, P. 1997. Principles and parameters: An
introduction to syntactic theory. Oxford, UK: Oxford University
Press.
- Downing, A. and Locke, P. 1992. English grammar: A
university course, second edition. London: Routledge.
- Greenbaum, S. and R. Quirk. 1990. A student's grammar of the
English language. Harlow, Essex, England: Longman.
- Groß, T. and T. Osborne 2009. Toward a practical dependency
grammar theory of discontinuities. SKY Journal of Linguistics
22, 43-90.
- Lockwood, D. 2002. Syntactic analysis and description: A
constructional approach. London: continuum.
- Ouhalla, J. 1994. Transformational grammar: From rules to
principles and parametrs. London: Edward Arnold.
- Quirk, R. S. Greenbaum, G. Leech, and J. Svartvik. 1979. A
grammar of contemporary English. London: Longman.
- Radford, A. 1988. Transformational Grammar: A first course.
Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Radford, A. 2004. English syntax: An intro